Die-Cutting Basics: Manufacturing 101
-
 By
Lee Lechner
By
Lee Lechner - May 4, 2021

Die-Cutting Basics
Industrial die-cutting is a widely used process for conververting a wide range of materials for a variety of different industries and applications. In order to correctly manufacture and/or source a die-cut project, it's improtant to understand the basics that go into this process.
In this post, we're going to take you through the fundamentals of what goes into die-cutting, including: What die-cutting actually is, forms of die-cutting, types of cuts, and tooling basics. So, let's get started...
What is Die-Cutting?
Die-cutting is the process of using a die (also referred to as tooling) to convert materials, such as rubber, pressure-sensitive adhesive tapes, foams, paper, plastics, and foil, by cutting, forming, and shearing.
With masking tapes, die-cutting is specifically used to convert pressure-sensitive adhesives into shapes, such as squares, rectangles, dots, discs, and a variety of other custom forms.
Forms of Die-Cutting
When it comes to industrial die-cutting, there are two main forms: Rotary and Overhead. These are two main forms that involve a physical die. That said, there are other ways of converting materials without the use of a die, such as a plotter, but we will not be covering those methods in this post.
Rotary Die-Cutting
Rotary die-cutting is a very cost-efficient and precise way of converting product at high-speed. The way it works is by using a cylindrical die to "kiss" cut shapes and leave them on a roll, similar to stickers.
Kiss-Cutting is when only the top layer of material is cut, therfore leaving teh bottom layer liner in tact.
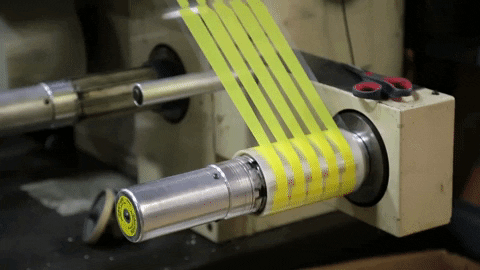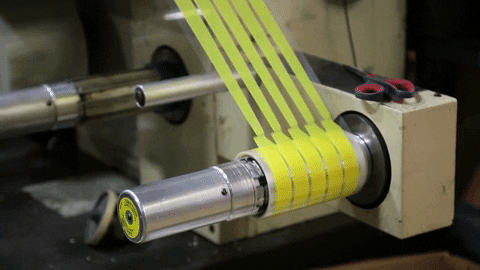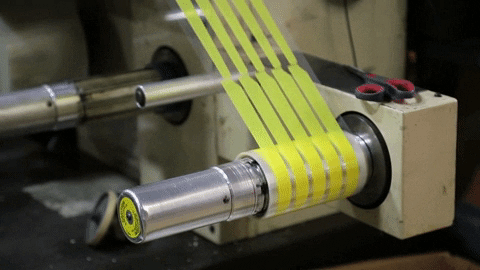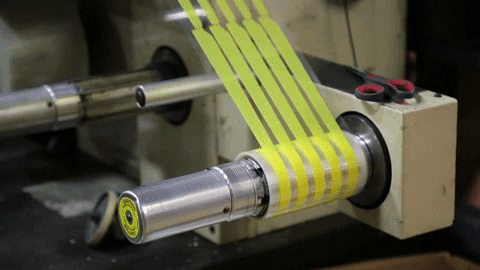

Overhead Die-Cutting
Overhead die-cutting is typically used for low volume or large parts. The way it works is a steel rule die is used to "through" cut parts into individual pieces, similar to cookie cutting.
Parts are typically split lined for easy installation (similar to what you'd see with a bandage).


Types of Cuts
Complete Cut
This cut results in cutting through all substrates, creating either a scrap piece or a final part (or both). This type of cut is commonly used for rubber gaskets/seals, where the final piece shape is cut and the exess material is thrown away or recycled.


Kiss-Cut
As mentioned earlier, a kiss-cut is when you cut through one substrate and stop at another (typically a liner/carrier). You can think of this as the stickers you may purchase where you peel the adhesive sticker off the roll you purchased.
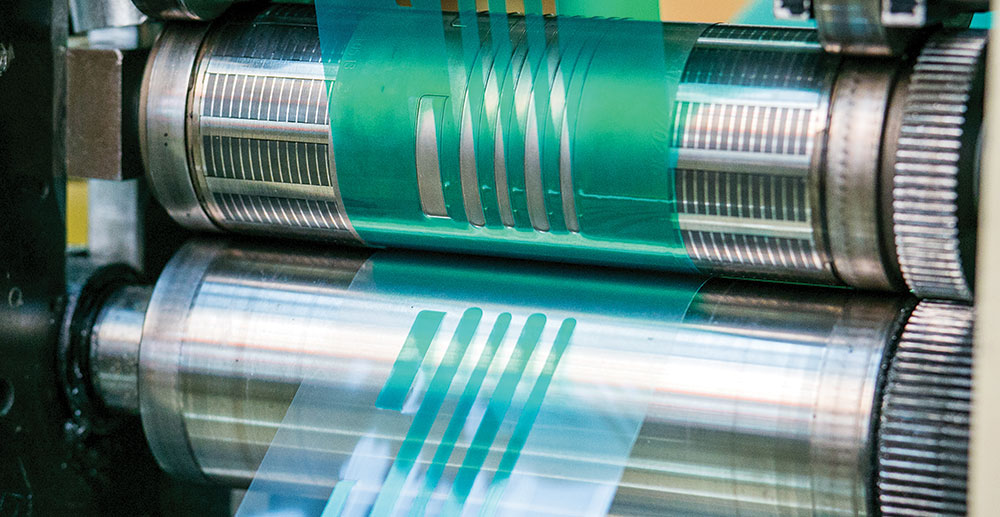

Die-Cut Tooling
Solid Tooling
Solid die-cutting tools are CNC machined steel cylinders that are surface hardened that use customizable blade angles
Pros:
- Long die-life
- Can be resharpened multiple times (auto or hand)
Limitations:
- Higher upfront cost
- Longer lead times due to CNC machining
- Tight geometry, sharp corners, and thicknesses above 0.125"


Flexible Tooling
Flexible die-cut tooling is made by chemically etching a flexible steel sheet, and then CNC sharpening the beveled edge. They can also be treated and hardened for extending the tool's life.
Pros:
- Cost-effective with a lower upfront cost
- Faster lead times
- A great option for tight geometry & materials less than 0.010" thick
- Moveable orientation and mag cylinder options
Limitations:
- Relatively shorter die-life
- Cannot be resharpened or repaired
- Cannot make full lineal cuts (continual around the circumference)


Magnetic Tooling
This is how flexible tools are utilized on rotary presses. These are machined cylinders that utilize powerful magnets to lock flexible tooling dies in place so that they do not lift or shift during the die-cut process.
The biggest pro of magnetic cylinders is their ability to significantly speed up setup times.
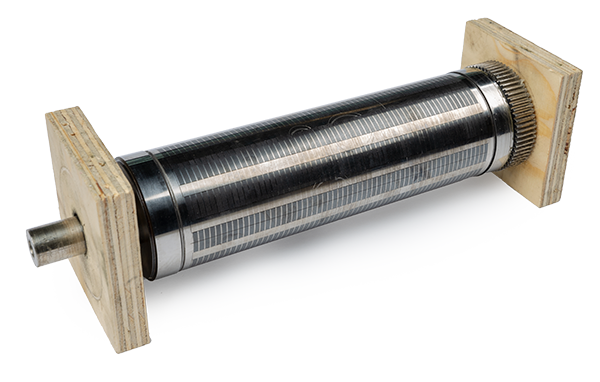

Steel Rule Dies
Steel rule dies are made with laser-cut and engraved boards with steel rule blades. With this option, you're able to customize the blades, blade angles, and treatment options.
Pros:
- Larger parts, thicker materials
- Medium die-life
- Can be re-ruled multiple times
- Very customizable specs (thickness and compression relationship)
Cons:
- Slow run-rate, resulting in higher labor costs


Conclusion
To sum it all up, die-cutting is an excellent method of converting materials, such as masking tapes, gaskets, seals, and much more. When it comes to industrial applications, you can break it down to the basics. You or the supplier you work with will need to factor in important factors, such as:
- Size of the die-cut
- Die-cut shape
- Estimated Annual Usage (EAU)
- Material (including material thickness)
Echo is highly experienced in die-cutting a variety of masking tapes, seals, and much more. If you're looking to discuss your next project, reach out to our team to get a quote started ASAP.









