Injection Molding Pricing: Domestic vs. Offshore vs. Hybrid
-
 By
Lee Lechner
By
Lee Lechner - Oct 4, 2023

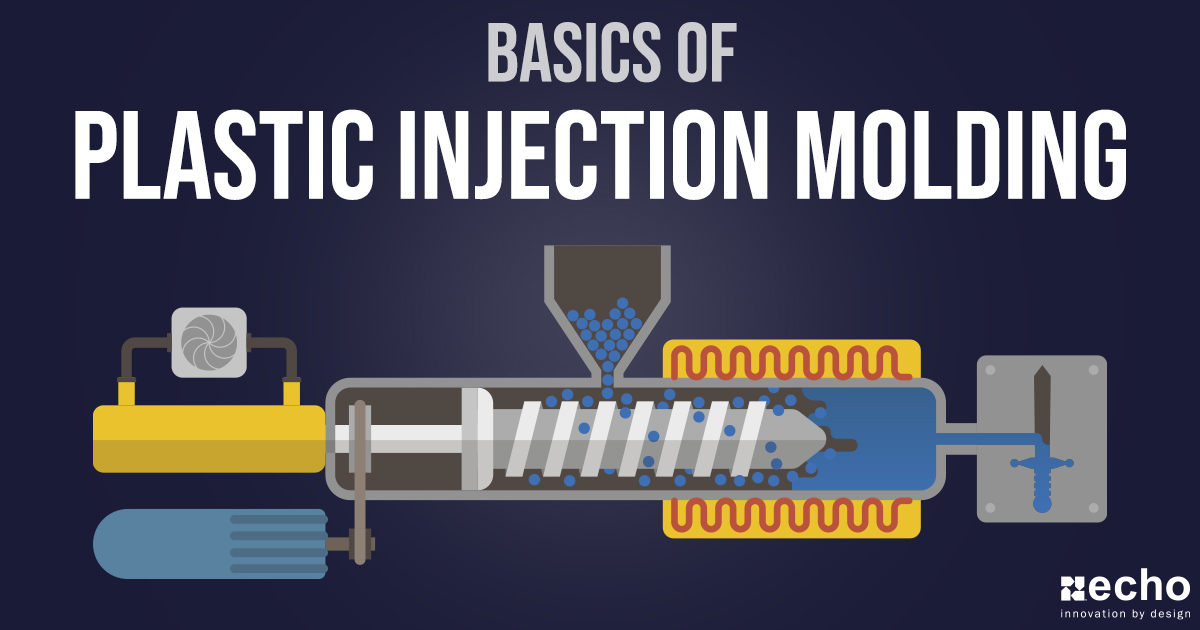
Injection molding is a widely used manufacturing process to create various plastic products and components. This process is crucial in industries ranging from automotive and electronics to medical devices and consumer goods.
When considering injection molding, manufacturers have two primary options: domestic and international production. In this blog post, we'll provide an in-depth comparison of domestic and international injection molding pricing, as well as a hybrid model, to give you valuable insights to help you make a more informed decision on your next project.
Primary Factors that Impact Plastic Injection Molding Costs
Before we get into pricing differentiation of domestic vs. offshore molding, it’s vital also to have a fundamental understanding of the primary factors that will play into the quote you receive.
- Part Size - The best way to think of this is larger parts require more resin, larger, more expensive molds, longer cycle times (increasing labor costs), and heavier final pieces (increasing transportation-related expenses).
- Part Complexity - Tight tolerances, surface finishing, and overall design complexity will all play a major role in pricing.
- Resin Used - Pricing on resins can vary greatly depending on what is chosen, as well as the resin’s quality, compounding, availability, and additives (such as glass fiber) used. Abrasive compounds will also impact the durability of mold, typically requiring a more expensive mold and lower mold lifespan
- Piece Quantity - Like many other large purchases, the more pieces requested, the more likely you’ll be able to receive bulk pricing discounts
- Mold Material - You’ll primarily see aluminum used for prototypes, as it can be machined much faster but is much less durable. Steel will likely be the choice for your full-production runs. Production duration and quantity of parts needed will play a role in the type of steel needed, impacting the price as well.
- Mold Cavities - More cavities will increase the initial cost of the mold, but it will also increase the efficiency (more parts being produced in less time), reducing production costs.
- Tooling Features - We won’t go in-depth here, but features such as mold runner, gating, de-gating, and ejection method will all be factored into pricing.
Domestic Injection Molding:
Pros:
- Lower Shipping Costs: Products manufactured domestically typically have lower shipping costs, especially for businesses located close to the injection molding facility.
- Quality Control: You have better control over the manufacturing process, allowing for higher-quality products.
- Production Lead Times: After tooling is finished and the first articles are approved, manufacturing domestically means you don’t have to deal with ocean freight logistics and customs.
Cons:
- Higher Tooling Costs: Tooling made in the United States will typically be between (roughly) 4-5 times higher than a mold sourced overseas (staying overseas) and roughly 2x more than an imported tool.
- Higher Labor Costs: Labor costs in developed countries are generally higher, which can increase production costs. Fortunately, injection molding is much less labor-intensive, especially when compared to rubber molding.
- Material Costs: Raw materials might be more expensive domestically due to factors like higher regulatory standards.
Our Thoughts On Domestic Injection Molding
More parts needed means more need to be shipped. This is a huge advantage for domestic injection molding due to transportation cost savings.
If your part is highly complex and needs to meet strict tolerancing and performance requirements, you’ll likely want to go domestic for several reasons. The main reason is that if modifications need to be made to the tool, support is nearby to make corrections.
Offshore Injection Molding:
Pros:
- Lower Tooling Costs: Mold material and labor to develop the mold itself will likely be much lower than domestic options.
- Lower Labor Costs: Labor costs can be significantly lower in countries with lower living standards.
Cons:
- Shipping Costs: Importing goods can incur substantial shipping costs, including tariffs, negating some cost savings (especially regarding high-volume parts)
- Quality Control Challenges: Ensuring quality control and consistency may be more challenging when manufacturing overseas. Meeting stringent quality standards may drive up production costs.
- Supply Chain Risks: As we’ve seen in recent years, there is always a risk of running into supply chain-related issues, such as fluctuation in container pricing, being held up in customs, ports being shut down, tariffs, etc.
- Production Lead Times: Ocean freight is the most cost-efficient way of transporting products from overseas. The huge drawback here comes from much longer lead times that can add anywhere between 4 - 12 weeks into the lead time.
Our Thoughts on Offshore Injection Molding
We typically recommend offshore molding for low-to-mid volume projects and for certain materials that we either can’t or won’t use domestically. With low volume, it will be much more difficult to offset the price of tooling domestically.
Hybrid Model: Offshore Tooling + Domestic Manufacturing
Pros:
- Tooling Costs: Offshore tooling will likely be a fraction of domestic options, making this a very appealing option to many, but you’ll still need to factor in shipping, as tooling weighs hundreds to thousands of pounds.
- Part Price Savings: Domestic manufacturing will result in cost savings from lower shipping charges and avoiding tariffs.
- Lower Production Lead Times: Once tooling is set up, production runs can be shipped directly to you instead of dealing with ocean/air freight from offshore sources
Cons:
- Shipping: While offshored tools may cost less, you’ll also have to factor in shipping charges associated with getting the tool to the domestic manufacturer. Depending on size, these tools will likely weigh hundreds, if not thousands, of pounds. Your two options will be via ocean freight (approximate lead time of 4-6 weeks) or air freight (approximate lead time of 2-3 weeks)
- First Article Lead Time: Due to the shipping factor mentioned in the last point, you’ll likely need to factor in additional timing before receiving the first article pieces.
Our Thoughts On Using A Hybrid Model
Importing a tool made overseas to have parts made domestically has become a more common go-to option, but you’ll want to plan ahead the time it takes to get the mold made, delivered, set up, and tested to meet project requirements.
Your biggest hangups on this will likely come from time constraints and how tight your tolerancing is, especially when it comes to complex parts. You’ll want to ensure you partner with an injection molder, like Echo, experienced in successfully launching hybrid model projects.
Project Example
A manufacturer requests a quote for an automotive clip project requiring a 4-cavity tool. Below, we’ll take you through tooling quotes, lead times, and piece pricing differences.
Project Lifespan: 5 Years
EAU: 100,000
|
Offshore (Tool + Molding) |
Domestic (Tool + Molding) |
Hybrid (Offshore Tool + Domestic Molding) |
|
| Lead Time (First Samples) | 7 - 9 Weeks | 12 - 13 Weeks | 17 Weeks |
| Tool Pricing | $7,500 | $45,000 | $30,000 |
| Piece Price | $0.99 | $0.82 | $0.82 |
| Part Total (Thru 5 Years) | $495,000 | $410,000 | $410,000 |
| Total Cost of Project | $502,500 | $455,000 | $440,00 |
As you can see above, while tooling is significantly cheaper offshore, piece price is much higher. Because of this, there is a $47,500 savings over the entire project's life! This is huge, especially because so many people might get hung up with the sticker price shock of domestic tooling.
For further cost savings, if the first article's lead time is acceptable, the customer is able to get an additional $15,000 in cost savings by going with a hybrid model.
Conclusion
The choice between domestic and international injection molding depends on various factors, including cost considerations, lead times, and quality requirements. Ultimately, both options have advantages and disadvantages, and the decision should align with your project needs, budget, and risk tolerance. Manufacturers often succeed by combining domestic and international production strengths to optimize their supply chains and meet diverse customer demands. Careful evaluation, strong communication, and thorough due diligence are essential when deciding between these two manufacturing approaches.